Introduction
As the world grapples with the escalating challenges of climate change, smallholder farmers find themselves on the front lines. With a deep understanding of the land and a commitment to the stewardship of our natural resources, these farmers are not just cultivators of crops but contributors to global food security. Yet, they are among the most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. This article sheds light on the plight of smallholder farmers, particularly in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. It introduces Ag BioTech’s innovative climate-smart agriculture solutions that are helping to empower these vital food producers against the looming threats of climate change.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), smallholder farmers operating on less than 5 hectares of agricultural land per household constitute a substantial portion of the world’s agricultural labor force and food production. In total, smallholder farm units contribute over 70% of food calories produced globally and account for a significant portion of the global production of many staple crops. These smallholder farmers are the backbone of communities globally and necessary contributors to our global food system, yet their ability to remain resilient to the changing climate is more critical now than ever.
Climate Change Impacts on Small Holder Farmers
Smallholder farmers in tropical and arid climates are facing the bulk of our shifting climate. The altering weather patterns and extreme climatic events including droughts and floods pose significant threats to their crops and livelihoods. The volatile environment has devastating impacts on crop growth, soil health, and water availability, especially in vulnerable regions where farmers have fewer resources to adapt to the threats of climate change. According to The International Monetary Fund (IMF), each increase of 1 degree Celsius correlates to a three-percentage-point reduction in agricultural output in developing countries.
The frequency and intensity of flooding events across the globe are expected to increase as the hydrological cycle amplifies with anthropogenic global warming, known as the Clausius-Clapeyron relationship. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) stated that both heavy and intense precipitation is projected to intensify and become more frequent in South, Southeast, and East Asia, with more intense fluctuation. As seen in the graph below, seasonal precipitation is estimated to continue to increase throughout the century with less annual stability under RCP4.5, a moderate scenario of greenhouse gas emissions.
Projected Mean Annual Precipitation in Southeast Asia.
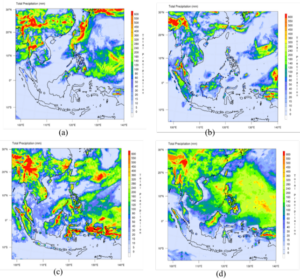
Total precipitation under RCP4.5 during January of 2013 (a), 2030 (b), 2050 (c), and 2070 (d). RCP4.5 is a moderate scenario where greenhouse gas concentrations are limited and stabilized by 2100 (APN).
Meanwhile in Sub-Saharan Africa, of the 30 worst climate events in history, 6 have taken place in the last 24 months. East Africa has just suffered a 40-year drought, followed by torrential rain which has flooded the sun-baked land; a result of the worst storm experienced in the last century, as found by Yale Climate Connections. Smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa are consistently navigating the environmental shifts between longer dry spells and an increase in cyclones that make landfall. The IMF forecasts crop yields in sub-Saharan Africa will decline by 5 to 17 percent by 2050, despite a rapidly growing population and already strained food security.
Global Food Insecurity
Smallholder farmers are the cornerstone of food production in many regions, yet the volatility of climate change threatens this critical role. As per recent FAO reports, the role of small farms in feeding the global population is monumental, with a majority of food calories consumed globally originating from these critical operations.
The chart below delineates the share of global staple crop production attributable to smallholder farms, illustrating the predominance of small farms in the production of rice, peanut, cassava, millet, sugarcane, what, maize, and soy — key staples that millions depend on.
Share of global production of major food crops in developing countries according to farm size
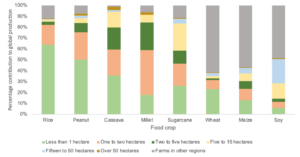
Percent of global production by mass of staple crops, originating from each agricultural land mass category classification (Zero Carbon Analytics, data from IOP Publishing).
According to the U.N. World Food Program, 170 million people in sub-Saharan Africa face severe hunger this year, with figures expected to rise as the disruption in resource availability continues to worsen. Globally, as many as 783 million people are hungry, and the World Bank warns that a 4-degree Celsius rise could escalate global hunger, impacting up to 1.8 billion people. Such a spike in food insecurity would disproportionately affect Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa — regions heavily reliant on smallholder farms for local food supply.
In Asia and the Pacific, small farms are responsible for roughly 80% of food consumption, while in Sub-Saharan Africa, they contribute up to 90% of the local food production. The centrality of these farmers in maintaining regional food security underpins the urgency for climate-resilient agricultural practices.
Currently, climate disasters are outpacing innovation. It is imperative that we collectively focus on agricultural development, identified as an essential component of the first Sustainable Development Goal of ‘Reducing Poverty and Hunger’, specifically regarding investments in small farms.
The Role of Climate-Smart Agriculture
In response to these challenges, climate-smart agriculture is a necessary adaptation to maintain a productive and profitable crop yield. Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is an approach that seeks to transform agricultural systems to effectively support food security in the new realities of a warming world. As per the World Bank, CSA involves three key pillars: sustainably increasing agricultural productivity, adapting and building resilience to climate change, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
“Climate change and food and nutrition insecurity pose two of the greatest development challenges of our time and yet a more sustainable food system can not only heal the planet, but ensure food security for all.” – World Bank, Climate-Smart Agriculture
Ag Biotech’s strategies and products directly align with CSA principles and promote a more sustainable agricultural landscape. For instance, our biofertilizers and biostimulants help increase crop resilience to climatic stressors, thereby ensuring consistent productivity even under adverse conditions.
In Vietnam, for instance, the use of BioShot has led to a 25% increase in rice yield, meanwhile in East Africa, Ag Biotech’s biofertilizers have been shown to increase maize yield by up to 30%, significantly enhancing food security and farmer income.
We can understand the positive impact that climate-smart agriculture has for farmers, by looking at the experience of Akello Grace in Dokolo District, Uganda. Grace is a 28-year-old farmer, who saw a 500% increase in maize yield, and a 460% yield increase in sorghum production after implementing CSA measures including bio-fertilizer usage, optimal weeding, and deploying a high-yield seed variant.
In Akello Grace’s words:
“I used to harvest a maximum of 4-5 bags (400-500 kgs) per acre for maize and 3-4 bags (300-400 kgs) for sorghum. Since enrolling with Agro Tourism Association (ATA) things have changed. In the training, they told us other varieties which can give you 4-5 times the bags I was getting. They taught us at the demo site how to plant seeds using plant nutrients (fertilizer) and why it’s important to do a timely weeding. After applying what I learnt, I was able to get 20 bags (2050 kgs) of maize (DK 777) and 14 bags (1400 kgs) of white sorghum (chromatin variety). This has greatly improved my income”
Enhancing Crop Yields and Supporting Farmers
Ag Biotech’s flagship products, BioShot and BioSeed, exemplify how targeted product design can revolutionize smallholder agriculture. These products improve productivity and contribute to the health and vitality of the land ecosystem through 4 main objectives.
- Sustainable Intensification: Our solutions are engineered to improve soil health and intensify crop production on existing land, making each square meter more productive and sustainable.
- Nutrient Availability: Our products are specifically designed to improve nutrient mobility, availability, and assimilation, to supplement fertilizer use for crops.
- Stress Reduction: Through the advanced formulations of our products, we tackle abiotic and biotic stress factors like drought and herbicide damage that are exacerbated by climate change, as well as preventing disease infection, thereby ensuring more resilient crop yields.
- Improved Quality: Our biostimulants not only boost yield but also improve crop quality, helping farmers meet the stringent export requirements, and thereby becoming more competitive on the global stage and increasing household income for smallholder farmers.
Ag Biotech understands the unique challenges of smallholder farmers and have designed our products for maximum efficiency and accessibility such as smaller packaging suitable for smallholder farmer use. The packaging presentations of Bio Seed and Bio Shot are tailored to a 1-acre (0.4 hectare) property, allowing farmers to optimize their investments for the necessary products, without purchasing more than needed. The effective packaging of our concentrated products makes it easier to ship globally to rural areas while minimizing shipping fees thus providing a more accessible product in ways that have historically been unfeasible for farmers in developing regions.
The user-friendliness of Ag Biotech’s product line also lowers the barrier to entry for use of these products. There are no maximum residue restrictions for these products, no human or environmental safety concerns, no phytotoxicity issues, and can be applied with standard small farm application means. This means that these products can be easily adopted in farmer’s practices without any concerns that conventional agrichemicals may carry.
Ag Biotech’s product offering has been pivotal for a successful yield increase for smallholder farmers in North America, the Caribbean, Africa, and Southeast Asia, with the anticipated extension into Europe, the Middle East, and Northern Africa. Our products have helped smallholder farmers improve their crop yield, income and livelihood, and remain resilient to the unpredictable changes in our global climate.
Ag Biotech’s Global Presence
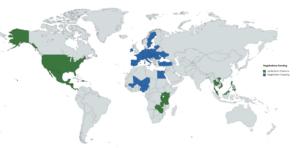
Global Presence of Ag Biotech as of 2023
Conclusion
In the complex challenge of global climate change, Ag Biotech stands as a committed advocate for smallholder farmers. Our mission extends beyond boosting crop yields, to cultivating a sustainable future through practices that strengthen the resilience of both the land and those who tend it. With innovative products and a strategic approach, we’re not only responding to the immediate needs but also anticipating the shifting paradigms of agriculture in a warming world.
Ag Biotech is dedicated to ongoing research and development, seeking ways to improve our products and strategies in response to the evolving needs of smallholder farmers and the changing climate. We recognize that our work requires collaboration, involving not just farmers and agricultural professionals, but also communities and global partners committed to sustainable development.
Contact Tristan Hudak, our Director of International Development, to discover how Ag Biotech’s products can directly improve your crop yield and build resilience in your community.
Email: [email protected] |
Resources:
APN. Climate change scenarios over Southeast Asia.
Climate change scenarios over Southeast Asia
IPCC. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/chapter/chapter-10/#:~:text=Both%20heavy%20and%20intense%20precipitation,et%20al.%2C%202021).
IOP Publishing.”Subnational distribution of average farm size and
smallholder contributions to global food production” https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/11/12/124010/pdf
Frontiers, Drivers of rainfall trends in and around Mainland Southeast Asia. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fclim.2022.926568/full
Frontiers. Contribution of smallholder farmers to food security and opportunities for resilient farming systems. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1149854/full
FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2023. https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc7724en
FAO. Climate Smart Agriculture Sourcebook, Adaptation & Mitigation. https://www.fao.org/climate-smart-agriculture-sourcebook/concept/module-a2-adaptation-mitigation/a2-overview/en/
World Food Programme. https://www.wfp.org/global-hunger-crisis
Yale Climate Connections. https://yaleclimateconnections.org/2023/05/five-of-africas-top-30-deadliest-weather-disasters-have-occurred-since-2022/
International Monetary Fund. “Climate Change and Chronic Food Insecurity in Sub-Saharan Africa”. https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/journals/087/2022/016/article-A001-en.xml
International Monetary Fund. “Boiling Point”. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/fandd/issues/2018/09/southeast-asia-climate-change-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions-prakash
Earth Stat. http://www.earthstat.org/
Zero Carbon Analytics. Smallholder farmers, agricultural sustainability and global food security. https://zerocarbon-analytics.org/archives/food/smallholder-farmers-agricultural-sustainability-and-food-security